
What is ERP? Meaning, Types, and Examples
Imagine a business where departments operate in silos, data is scattered across different systems, and valuable insights are buried under mountains of spreadsheets. This fragmented landscape can hinder collaboration, slow down decision-making, and ultimately impede growth.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). It's an integrated software solution that acts as the central nervous system of your organization, unifying and streamlining various business processes across departments.
An ERP solution consists of a group of tightly knit modules that help facilitate operations in different departments like inventory and warehousing, PPC, production, accounts and finance, HR, and supply chain management.

What is ERP? Introduction to Enterprise Resource Planning
Imagine running a company where each department uses its own software and spreadsheets – finance, sales, inventory, manufacturing, and HR – all isolated. Data gets duplicated and out of sync, making it hard to get a clear picture of your business. ERP stands for enterprise resource planning, and it’s the antidote to this chaos
An ERP system is an integrated management platform that unifies all the processes needed to run a company into one coherent system.
In simple terms, ERP software brings together core functions like accounting, inventory management, production, sales, and HR in a single database. This creates one single source of truth across the organization, allowing everyone to work with the same real-time information. By centralizing data and workflows, enterprise resource planning systems eliminate silos and streamline the core business processes of an organization. An ERP is a centralized management system that integrates data from all departments – enabling real-time visibility and informed decision-making across the business.
An ERP solution is a modular software application suite that talks to each other through a shared database. ERP systems were initially coined in the 1990s as an evolution of earlier manufacturing resource planning tools (MRP) to cover enterprise-wide processes beyond just production
Modern ERP software can handle everything from tracking raw material purchases to managing customer orders and financial reporting – all in one place. Before we dive into specific ERP modules and benefits, let’s overview the main types of ERP systems available today.
Think of ERP as a single platform that connects:
✔︎ Finance and Accounting: Manage your finances, generate reports, and ensure compliance. Effective financial management allows you to make informed decisions and facilitates strategic planning for sustainable growth.
✔︎ Inventory and Warehouse Management: Track stock levels, optimize orders, and streamline fulfillment. Optimizing orders and streamlining fulfillment processes reduces costs and enhances customer satisfaction through timely delivery.
✔︎ Sales and Marketing: Manage customer relationships, automate marketing campaigns, and track all your leads. Automating marketing campaigns can significantly increase efficiency and effectiveness, leading to better customer engagement and higher conversion rates.
✔︎ Human Resources: Handle payroll, manage benefits, and track employee performance. Tracking employee performance ensures accountability and facilitates continuous improvement and talent development within the organization.
✔︎ Production and Supply Chain: Plan production schedules, manage resources, and ensure on-time delivery. Efficient production scheduling and resource management are essential for minimizing costs and maximizing productivity, ultimately ensuring timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
What Makes a Good ERP System?
ERP is not just software; it's a strategic investment in the future of your business. ERP can help you achieve sustainable growth and gain a competitive edge by unifying your operations, improving efficiency, and empowering data-driven decision-making. Choosing the right ERP system is crucial for your business success. Consider these key factors:
✔︎ Scalability: Can the system grow with your business?
✔︎ Customization: Can it be customized to fit your specific needs?
✔︎ Integration: Can it integrate seamlessly with your existing systems?
✔︎ Security: Does it offer robust security features to protect your data?
✔︎ Ease of use: Is it user-friendly and intuitive for your employees?
What are the ERP system types?
ERP solutions come in various flavours to cater to the diverse needs of businesses. Here are the main types:
✔︎ On-Premise ERP:
Traditionally, ERP systems were installed on a company's servers, requiring significant upfront investment and IT expertise. Traditional on-premise ERP systems often necessitate substantial initial capital investment in hardware and specialized IT personnel for installation, customization, and ongoing maintenance. This approach gives companies complete control over their data and systems but may entail longer implementation times and higher associated costs.
✔︎ Cloud-based ERP:
The vendor hosts These solutions on remote servers, offering greater accessibility, scalability, and lower upfront costs. Cloud-based ERP solutions allow businesses to access their systems and data from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and facilitating collaboration across geographically dispersed teams. Moreover, the subscription-based pricing model of cloud ERP typically eliminates the need for large upfront expenditures, making it particularly attractive for small to medium-sized enterprises seeking to minimize initial costs while benefiting from robust ERP functionality. For example, a company looking to scale rapidly might opt for a cloud-based ERP solution like NetSuite due to its scalability and accessibility.
✔︎ Hybrid ERP:
This combines on-premise and cloud-based deployments, allowing companies to maintain control over sensitive data while leveraging the benefits of the cloud. While hybrid ERP systems offer a blend of on-premise control and cloud-based flexibility, they also come with their own set of challenges and disadvantages:
• Complexity: Managing a hybrid ERP environment requires integrating on-premise and cloud systems. This complexity can increase IT teams' workload and necessitate specialized expertise to ensure smooth operation.
• Integration Issues: Integrating on-premise and cloud systems can sometimes lead to compatibility issues or data synchronization problems. Ensuring seamless communication between different components of the hybrid ERP system may require additional customization and ongoing maintenance.
• Security Concerns: Hybrid ERP environments may introduce security vulnerabilities, particularly at the interfaces between on-premise and cloud systems. Companies must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, which can be challenging to manage across disparate systems.
NetSuite vs. On-Premise ERP
NetSuite stands out as a powerful and scalable ERP solution specifically designed for the needs of growing businesses. NetSuite is built on a modular structure. This means businesses can start by implementing the core modules essential for their current operations, such as financials, inventory management, or customer relationship management (CRM). As a business expands, new modules can be seamlessly added to support additional processes like e-commerce, project management, or human resources. By empowering you with scalability, flexibility, and powerful features, NetSuite helps you unlock your full potential and achieve sustainable success.
✔︎ Faster implementation: NetSuite's cloud-based deployment model allows for a quicker and more cost-effective implementation compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
✔︎ Reduced IT burden: Eliminate the need for extensive IT infrastructure and staff with NetSuite's fully managed service.
✔︎ Automatic updates: Benefit from ongoing updates and enhancements without the need for manual intervention.
✔︎ Accessibility: Access your data and applications from anywhere on any device.

Core ERP Modules and Functions (Focus on Manufacturing & Supply Chain)
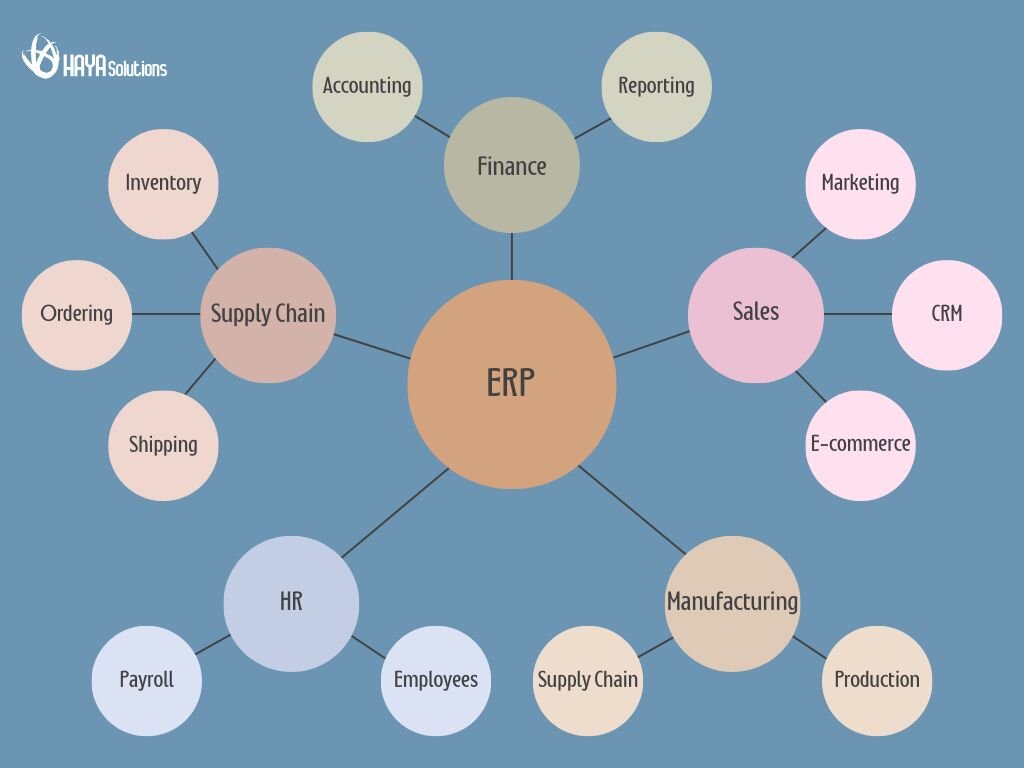
One of the strengths of ERP is its modular design. You can think of ERP modules as different functional units or apps within the ERP that handle specific business areas. These modules share information through the central ERP database, meaning departments that used to be isolated can now collaborate with the same data. Here are the core ERP modules you’ll typically find, with an emphasis on manufacturing and supply chain management:
✔︎ Financial Management (Accounting):
The finance module tracks all accounting transactions, including general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting. It is the backbone of any ERP and ensures you can monitor profitability and cash flow in real time. With ERP, financial data from sales, production, or procurement is automatically reflected in the books, reducing manual data entry and errors.
✔︎ Human Resources (HR):
The HR module manages employee information, payroll, benefits, and often recruiting or talent management. In the ERP, HR can connect staffing costs and data to the rest of the business. For example, when HR onboards a new employee, that data can flow into user permissions for other modules or labour cost calculations in the finance module.
✔︎ Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Many ERP systems include or integrate with a CRM module. This module handles sales orders, customer information, leads, and support. Linking CRM with ERP means that when a sales rep closes a deal, the order can automatically flow into finance for invoicing and into the warehouse module for fulfillment. It ensures that the sales pipeline and revenue forecasts are based on the same data as production and finance, truly unifying the core business processes.
✔︎ Inventory Management & Procurement:
Inventory management is often part of a broader supply chain module. It tracks warehouse stock levels, monitors stock movements, and assists with purchase ordering. Procurement tools help automate purchasing raw materials or goods when inventory is low or demand forecasts rise. An integrated ERP module ensures purchase orders, inventory receipts, and supplier data are all updated in real time across the system. This prevents situations like production scheduling, which the inventory module shows as out-of-stock since all data is connected.
✔︎ Manufacturing & Production Planning:
The manufacturing module (sometimes called the Production or MRP module) is critical for companies that make products. It plans production schedules, manages work orders and bills of materials, and tracks the transformation of raw materials into finished goods. In an ERP, the production schedule can automatically consider current inventory, pending purchase orders, and sales demand. For example, if sales orders spike, the ERP can signal the production module to adjust schedules and prompt procurement to buy more raw materials. This close linkage between manufacturing, supply chain, and finance helps maintain optimal production without overstocking or delays.
The ERP’s real-time updates allow supply chain managers to respond quickly if there’s a materials shortage or a machine downtime, minimizing downtime across the board.
✔︎ Supply Chain Management (SCM) & Logistics:
This encompasses procurement, inventory (as mentioned), as well as warehouse management, order fulfillment, and shipping. A supply chain module in ERP coordinates the end-to-end flow of materials and products, from supplier procurement to warehousing to delivering products to customers. Using an ERP system with integrated supply chain features gives the company visibility into each product lifecycle stage. For instance, managers can track the status of a purchase order for a component, see when it arrives in the warehouse, and ensure it’s allocated to production jobs – all within one system. According to Oracle, this unified view helps procurement managers buy the right quantities of raw inputs and keep costs under control.
It also means fewer delays: the ERP can alert planners to adjust production or inform customers proactively if a shipment is late.
✔︎ Others (Project Management, etc.):
Depending on the business, there are many other modules an ERP can include – project management for professional services firms, enterprise asset management for maintenance of equipment, e-commerce modules for online sales, and more. The key is that all these modules feed into the same ERP database. If your business adds a new process, you can often plug in a new module without setting up a separate system.
Typical ERP modules cover everything from sales and CRM to procurement, production (PLM), distribution (SCM), accounting, HR, and more – connected through a central database.
Having these modules under one roof allows an ERP enterprise resource planning system to break down the walls between departments. For example, the manufacturing supply chain team can see updated sales forecasts and inventory levels. In contrast, the finance team sees current manufacturing costs and purchase commitments. Every module shares real-time data, significantly improving coordination and decision-making. We’ll discuss those benefits more next.
Get a free consulting
Benefits of ERP Implementation (Real-Time Data, Efficiency, and More)
Why do companies invest in ERP? When implemented well, an ERP can be transformative for a business. Here are some of the top benefits of ERP implementation:
✔︎ Integrated Information & Single Source of Truth:
With ERP, all your data is stored in one place (or seamlessly connected through one system). This creates a single source of truth for the organization.
Everyone from the CEO to an inventory clerk works with the exact up-to-date figures, whether yesterday’s sales or current stock levels. This consistency eliminates the confusion of conflicting spreadsheets and ensures that business decisions are based on reliable data. For instance, sales and production managers can view the same real-time order status and inventory data, avoiding miscommunication. As one source notes, companies use ERP to connect data from multiple business functions in a centralized system, using the same data to maintain a single source of truth.
✔︎ Real-Time Data for Better Decision-Making:
Real-time data is a game changer. In traditional setups, you might only see financial reports at month-end or manually aggregate inventory reports weekly. ERP systems update information continuously as transactions happen. This means managers and even automated workflows can respond immediately to new information. For example, an ERP can trigger an alert to procurement when a raw material stock hits a reorder point, or provide up-to-the-minute sales dashboards to executives. Having real-time visibility into operations helps in spotting trends or issues early. It’s reported that because ERPs can access real-time data across the company, they uncover impactful trends and provide extensive business insights, leading to better and faster decision-making
✔︎ Efficiency and Automation of Processes:
ERP implementation often brings a considerable boost in efficiency. By automating routine tasks and integrating workflows, ERPs cut down on manual work and errors. For instance, when an order is entered, the system can automatically schedule it for production, deduct the inventory, generate an invoice, and update revenue forecasts without human handoffs. This streamlining speeds up processes (think shorter order-to-cash cycles) and frees employees from tedious data entry to focus on higher-value work. Companies commonly save time and money by automating manual processes and reducing errors with ERP.
Less double-entry of data means fewer mistakes (like mismatched orders or incorrect inventory counts) and less time spent correcting those mistakes.
✔︎ Improved Collaboration & Communication:
With an integrated system, collaboration between departments improves naturally. When every department can see what others are doing (within appropriate permissions), working together is more effortless. Sales can check product availability instantly, warehouse teams can see upcoming orders, and finance can see expenditures committed by purchasing – all without a flurry of emails. ERP’s centralized data and standardized processes foster interdepartmental cooperation because everyone effectively uses one big platform rather than many disparate tools.
✔︎ Enhanced Reporting and Analysis:
ERP systems often include robust reporting and business intelligence tools. Because all the data is in one database, generating comprehensive reports is much easier than pulling data from multiple sources. Users can create dashboards that draw on finance, sales, and operational data together, giving a 360-degree view of performance. Over time, this can highlight inefficiencies or profitable trends that were hard to see. For example, you might discover through an ERP report that a particular product’s profit margin is shrinking due to rising raw material costs, prompting you to find a new supplier or adjust pricing.
✔︎ Regulatory Compliance and Data Security:
Many ERP solutions have built-in compliance management for financial standards, industry regulations, and data security protocols. With a single system, it’s simpler to enforce security policies and track who did what in the system (for audit trails). This is particularly useful for businesses in regulated industries or those following data protection standards like GAAP, IFRS, or GDPR. Instead of managing compliance in multiple systems, an ERP can provide centralized control and documentation.
In short, an ERP implementation can lead to process efficiency, cost savings, and better decision-making driven by real-time, trustworthy data. It’s not just about IT software – it’s about running your business more effectively. Of course, to reap these benefits, the implementation has to be done right. ERP projects can be complex, so having a clear plan is essential. In the next section, we outline a structured guide to ERP implementation.
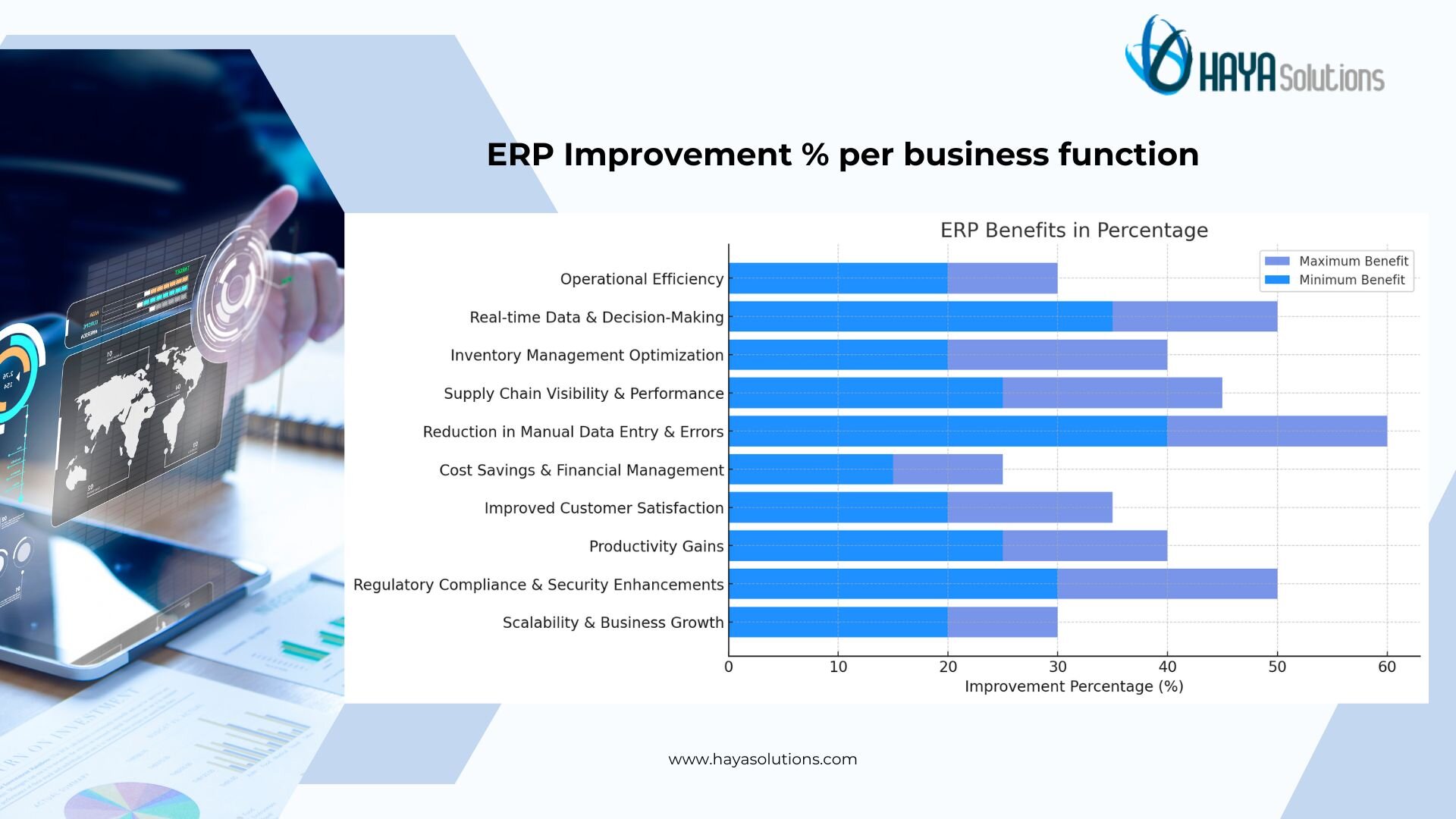
Real-time dashboards and integrated reports are a key benefit of ERP. When enterprise resource planning systems consolidate data, decision-makers get instant insights (like the charts above) that help drive efficiency and growth.
ERP Implementation Guide: Key Steps for Success
Implementing an ERP is a significant project that touches almost every part of your business. It’s not as simple as installing software; it involves rethinking processes and careful change management. Below is a structured ERP implementation guide outlining the key steps and best practices to increase the chances of a successful rollout:
1- Discovery and Planning:
Start by clearly defining your objectives and requirements. What problems must the ERP solve? Which core business processes will it cover? Assemble an internal project team with stakeholders from all departments (finance, operations, IT, etc.) and secure executive sponsorship. During this phase, map out your current processes and identify pain points (e.g., duplicate data entry, lack of visibility, delays). It’s crucial to set a realistic budget and timeline. Planning is the foundation – a well-defined scope and strong leadership support will guide the project to success.
2- ERP System Selection:
With requirements, evaluate ERP vendors or solutions that fit your business size and industry. Decide on the type of ERP (on-premise vs. cloud) that aligns with your IT strategy. Key factors include functionality (does it have the modules you need, like manufacturing or CRM?), scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and cost. Internal linking recommendation: Refer to our guide on choosing the right ERP solution for a detailed comparison of options and what to ask vendors during selection. In this stage, involve end-users in getting feedback through demos and ensure the ERP can adapt to your specific workflows (or note what processes you might adapt to fit the ERP). Selecting the right partner or ERP vendor is critical – an experienced implementation partner (like Haya Solutions) can help tailor the system to your needs and provide industry insights.
3- Design and Process Alignment:
Once you’ve chosen an ERP, the next step is system design and process alignment. This means figuring out how your new ERP will handle each business process. Re-engineer processes to follow best practices built into the ERP – you don’t want to simply recreate old inefficient steps in a new system. For example, decide how the sales order workflow will move from the sales module to inventory to finance within the ERP. Identify any gaps between the ERP’s standard functions and your requirements: can they be addressed through configuration, or do they need customization? Minimizing heavy customizations is usually wise (to keep the system upgradable and reduce complexity). Document the future-state processes and get agreement from process owners in each department. This blueprint will guide the actual system setup.
4- Configuration and Data Migration:
The ERP system is set up (often in a test environment) according to the design. Configuration involves adjusting settings in the software: defining your chart of accounts in the finance module, setting up approval workflows, inputting roles and permissions for users, and so on. Meanwhile, you must prepare for data migration – moving all relevant data from old systems into the ERP. This includes customers, suppliers, product lists, inventory levels, open orders, financial balances, employee records, etc. Data migration is critical: you must clean the data to eliminate duplicates or errors before importing. Often, companies will extract data to spreadsheets, cleanse and format it, and then use the ERP’s import tools to load it. It’s wise to do trial migrations and verify data integrity. After configuration and data loading, you’ll have a working ERP system with your business data ready for testing.
5- Testing (Iteration):
Thorough testing is essential to catch issues before going live. This typically includes unit testing (each module works correctly on its own), integration testing (modules work together on end-to-end scenarios), and user acceptance testing (key users perform day-to-day tasks in the system to ensure it meets their needs). For example, you might test a complete order-to-cash cycle: create a sales order, allocate inventory, generate an invoice, and receive payment – verifying that each step flows correctly through the ERP. Any bugs, mismatched data, or workflow problems should be addressed now. It’s common to go through multiple iterations of fix and re-test. This step builds confidence that the ERP will support your business correctly. Fixing problems in the test phase is much easier than after the system is live.
6- Training and Change Management:
Even the best ERP won’t deliver benefits if users don’t know how to use it. Training your staff on the new system is a pivotal part of implementation. Develop training materials tailored to each user role (accountants get different training than warehouse managers, for instance). Use a combination of methods – workshops, hands-on sessions, documentation, and maybe a test sandbox where users can practice. In addition to software training, focus on change management: communicate early and often about why the company is implementing an ERP, how it will improve everyone’s work, and address concerns. People will have to change some habits and processes, which can be challenging. Having leadership emphasize the importance and benefits of the new system and possibly selecting change champions in each department can help drive user adoption. The goal is to have your team comfortable and proficient with the ERP by the time you go live.
7- Go-Live and Deployment:
This is when you transition from old systems to the new ERP. Plan the go-live carefully to minimize business disruption. Decide on a go-live strategy – will it be a “big bang” (all modules and locations switch over at once on a set date) or a phased rollout (e.g., one module or department at a time)? Each approach has pros and cons. Before going live, ensure all final data (like ending inventory balances or open invoices from the legacy system) is migrated so the new ERP is current. It’s common to run the new system in parallel with the old for a short period for validation, but ultimately, you’ll cut over completely. Have your project team and vendor/consultants on standby to support any issues during the cutover. Expect a few hiccups – maybe some missing data or user errors – and be ready to solve them quickly. With good preparation, you’ll get through this phase with manageable stress.
8- Post-Implementation Support and Optimization:
The ERP is live, but the project isn’t entirely over. In the weeks and months after going live, support users as they encounter questions or minor issues. It’s wise to have internal or external ERP experts to troubleshoot and ensure everything runs smoothly. Use this period to gather feedback: are there features people aren’t using effectively? Are there process bottlenecks the ERP revealed that you can now address? Once users are comfortable, you’ll often find opportunities to optimize your processes further or enable additional ERP modules that weren’t critical for going live. Plan for regular system maintenance, future updates (especially if it’s a SaaS ERP, which might update automatically), and continuous training for new hires or advanced features. Over time, you can leverage more of the ERP’s capabilities – for example, implementing advanced analytics or adding a CRM module – to continuously derive more value from your ERP investment.
Following these steps provides a roadmap for ERP implementation. Every business is unique, so adapt the plan as needed. The key is strong project management and involvement from your team at every stage. An ERP implementation is not just an IT project; it’s a business transformation project. With careful planning, the right ERP partner, and stakeholder commitment, you set the stage for ERP success. (Internal linking tip: If you need assistance with any phase of an ERP project, consider contacting a professional ERP implementation service provider.)

Conclusion: Transforming Your Business with ERP
In summary, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a powerful tool that can integrate all your disparate business functions into one cohesive platform. An ERP system provides a holistic, real-time view of your business by uniting ERP modules for finance, HR, sales, and especially manufacturing supply chain operations. We discussed how ERP stands for enterprise resource planning, which essentially means planning and managing all enterprise resources (money, people, materials, information) through integrated software. A well-chosen ERP solution acts as the nervous system of your company – coordinating activities, improving efficiency through automation, and supplying real-time data for better decision-making. Whether delivered on-premise or as a cloud-based SaaS solution, ERP software becomes the single source of truth for your organization, eliminating data silos and aligning teams toward common goals.
Implementing an ERP is undeniably significant, but the benefits – from streamlined processes and cost savings to improved collaboration and insights – make it worthwhile. The key takeaways from this guide are: understand your needs and ERP options (types), ensure the system covers your core business processes, involve all stakeholders in a structured implementation approach, and don’t skimp on training and change management. With those in place, an ERP implementation can transform your business processes and position your company for scalable growth.
Has this overview answered your questions about what ERP is and why it matters? If you’re considering an ERP for your organization, remember that planning and the right expertise are crucial. Feel free to contact us at Haya Solutions – we’re happy to discuss how enterprise resource planning systems could fit your business and help you navigate the next steps. Together, we can turn ERP from a complex concept into a game-changing reality for your company. Let us know your thoughts or questions in the comments below, and if you’ve gone through an ERP journey, what lessons did you learn? We’d love to hear your experiences and help you on your path to a successful ERP solution.


