![Food Manufacturing: Plan, Plan, and Plan! [Part 1]](https://cdn.builder.io/api/v1/image/assets%2F47213b9171d748bd93ee9f6f18e9f56c%2Fb872c24b51f040638e6bc452d97f3ef3)
During times of uncertainties, planning plays a critical role in the survival of businesses, especially the Food Manufacturing industry which heavily relies on external economic and socio-economical factors. Vital survival advice I was taught back in the days while studying Engineering, it’s always handy to go back to the fundamentals to overcome unexpected situations! We will dig our way through planning by building a framework based on supply chain fundamentals.
A PLANNING FRAMEWORK?
While all manufacturer implements some form of Manufacturing Planning and Control (MPC) system – which is concerned with the planning and controlling of all aspects of manufacturing, including procurement of raw material, scheduling the production, and shipping to customers -the success of the business needs to implement a practical MPC framework.
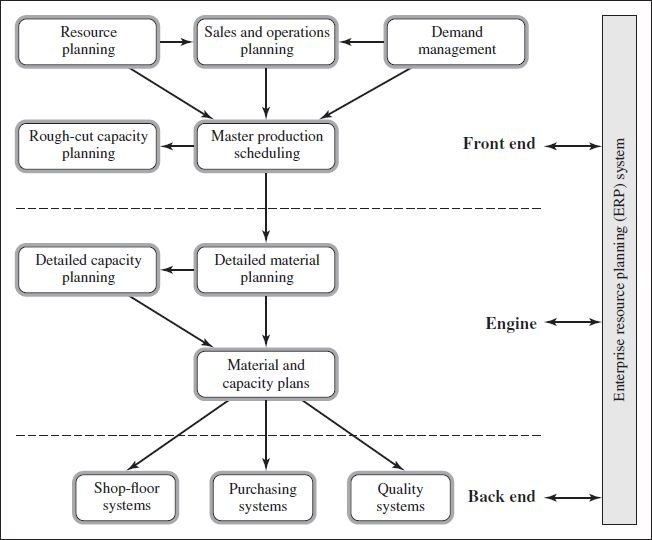
LET’S TAKE A STEP BACK FIRST!
The main goal of businesses is to maximize the long-term financial performance and the value to their shareholders, with other stakeholders, considered. Many metrics measure financial performance; we will focus on one metric called Economic Value Added (EVA), which measures company profits over the cost of capital (debt and equity), which, when compared to other metrics, is an internal and management-controllable measure [Source: Kay, I., Madu, M., & Johnson, P. (2020, March 8). Assessment of ISS’s Use of EVA in CEO Pay-for-Performance Model. The Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance.
There’s no profit unless you earn the cost of capital – Alfred Marshall.
Let’s lay it down first, EVA is a measure of Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT), less cost of capital; that measure can be expressed by the Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) and the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), multiplied by the Capital Employed (CE):
- EVA = (ROCE - WACC) x CE
- ROCE = NOPAT / CE
UGLY FORMULAS, PRETTY VISUALIZATION
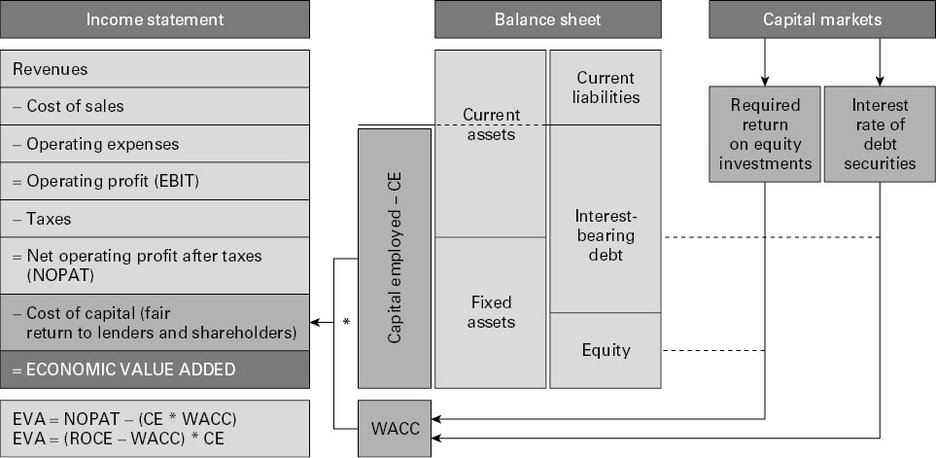
Value won’t be created unless revenue exceeds all costs, including the cost of capital; in simpler terms, ROCE has to exceed WACC, but how can a business achieve that?
In our article, we will focus on measurable and Supply/Demand-related factors such as:
- Higher Revenue
- Lower Cost
- Lower Working Capital
On the one hand, to achieve high revenue from a demand perspective, businesses, and food manufacturers, in particular, need to reduce their stock-outs. And to lower their costs, they need to reduce their inventory carrying charge, cost of material, distribution costs, etc.
On the other hand, to lower working capital, businesses need to optimize their Cash-to-Cash (C2C) cycle time – a metric describing the average days required to turn a dollar invested in the raw material into a dollar collected from a customer -and one vital factor in optimizing the C2C is reducing safety stock levels.
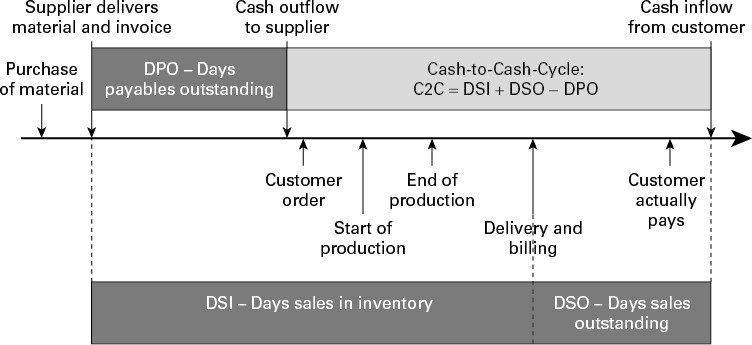
While the three factors might look contradictory, this is where MPC comes in place; the effectiveness of an MPC framework is to balance the trade-offs of the three factors to support supply chain initiatives and potentially achieve the business’s ultimate goal to increase the value for shareholders.
A CONTRADICTION, YET MANAGEABLE!
Back to our MPC framework, there are three main entry points, Demand Management, Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) and Resources Planning; in our article, we will focus on Demand Management and S&OP and explore an overview of Demand Planning and how technology can add value to the overall MPC framework.
S&OP balances a company's sales and marketing activities with its production, ensuring that manufacturing will support its sales activities and strategy. Demand Management is the business gateway to marketplaces (Customers); it allows businesses to do activities such as forecasting customer demand, order management, communicating back promises of delivery, and orders statuses and changes [Source: Jacobs, Robert F., William L. Berry, Clay Whybark, and Thomas E. Vollmann. 2018. "Demand Management in MPC Systems." Chap. 3.1 in Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management: The CPIM Reference. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.].
Demand Management must conform to the business strategy, manufacturing capabilities, and customer needs, and those factors define different MPC environments. A fundamental classification of an MPC environment is Customer Order Decoupling Point (COPD).
The CODP is the point in the material flow where the product is tied to a specific customer order [Source: Olhager, J. (2010, December). The role of the customer order decoupling point in production and supply chain management. Computers in Industry, 61(9), 863–868.]; E.g., When a customer buys cereal off the shelf in a retail store, the CODP is the finished good (Cereal), but when a customer orders custom-made cereal (for example, U-RAAW! Health Foods), the CODP is now the raw material, meaning it moved further down the supply chain.
It's critical to understand the role of CODP and different manufacturing situations such as make-to-stock (MTS), assemble-to-order (ATO), make-to-order (MTO), and engineer-to-order (ETO). CODP divides the flow into two categories upstream – forecast driven -and downstream – customer order driven – allowing manufacturers to adopt different situations for various products.
We will focus on CODP in the dominant manufacturing situation of food manufacturing businesses (MTS) and how it fits within the supply chain planning matrix (Stadtler and Kilger, 2000).
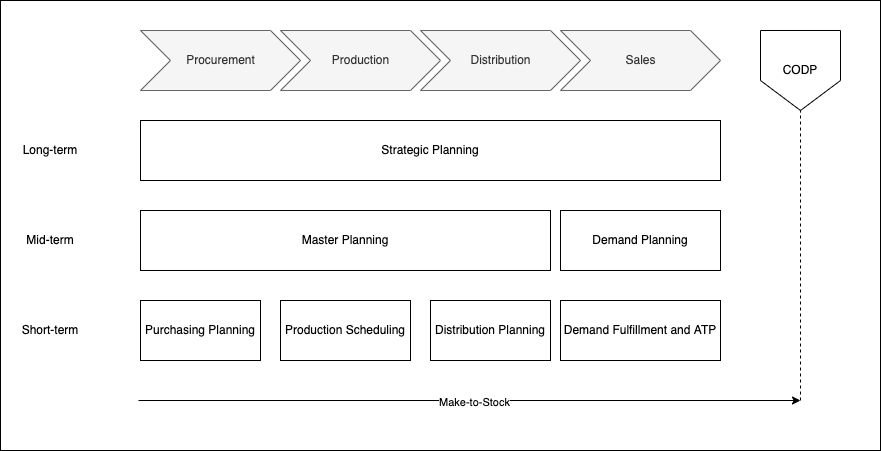
WORKING OUR WAY BACKWARDS, INTRODUCING DEMAND PLANNING!
To maximize EVA, we mentioned three factors, Higher Revenue, Lower Cost and Lower Working Capital. The main goal of Demand Planning is to identify the sweet spot to maintain optimal stock levels that would minimize inventory carrying costs and material costs.
In the future article, we will explore the tools and techniques of Demand Planning and how we can apply them in Oracle NetSuite, leaving you now with an introduction to Oracle NetSuite Demand Planning:
WANT TO DISCUSS FURTHER?
Working with a partner who understands your business and the product is essential. We at Haya Solutions Inc. pride ourselves on a track record of successful ERP implementations. With +25 years of combined experience in many verticals such as Manufacturing, Wholesale Distribution, Retail, Medical Equipment, Construction, Insurance, Healthcare, e-Commerce, and many more, working with customers in private and public Small and Medium Enterprises.


